FAQs
Mobile First, How It Works in CSS
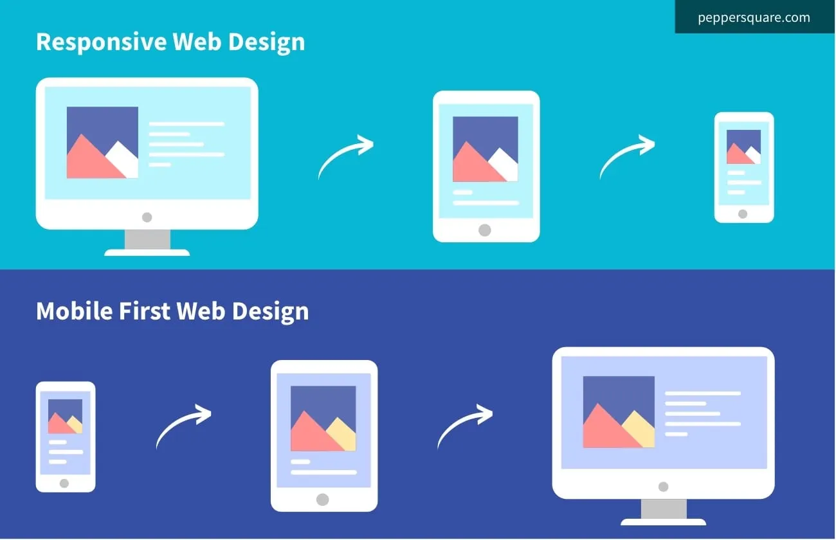
Instead of starting with desktop styles and then overriding them for mobile, you flip it:
mobile-first.css
// media aliases and breakpoints
$screen-sm-min: 600px; // Extra small (mobile) and up
$screen-md-min: 744px; // Tablet Portrait and up
$screen-lg-min: 1024px; // Tablet Landscape and up
$screen-xl-min: 1280px;
Example Conversion
Desktop-first code:
desktop.css
.card {
display: flex;
gap: 2rem;
}
/* Adjust for mobile */
@media (max-width: 600px) {
.card {
display: block;
gap: 1rem;
}
}
Converted to mobile-first:
mobile.css
.card {
display: flex;
gap: 2rem;
/* Adjust for mobile */
@include sm{
display: block;
gap: 1rem;
}
}How to Convert a Desktop-First Site into Mobile-First
Start from your base CSS:
Remove all “desktop” assumptions as defaults. Write default styles for mobile (single column, smaller paddings, stacked layouts).
Flip your media queries:
Replace @media (max-width: …) with @media (min-width: …).
Example:
desktop.css
@media (max-width: 768px) { … }
→ @media (min-width: 768px) { … }Simplify defaults:
- Typography: smaller font sizes by default.
- Layout: stacked / vertical by default.
- Spacing: tighter margins/paddings by default.
Progressively enhance:
- Add columns, grids, sidebars only when screen is wide enough.
- Use min-width breakpoints to scale up.
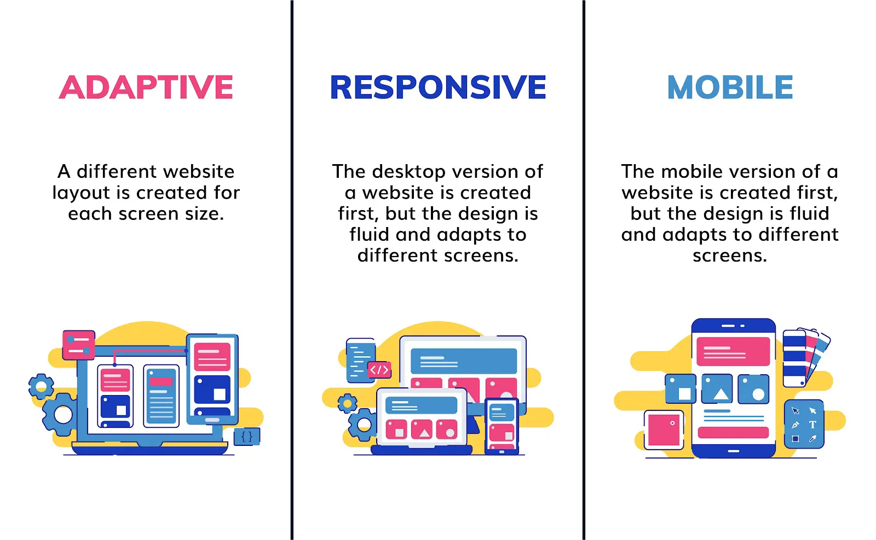
Javascript using Min width media queries to enhance the experience for larger screens.
const mq = window.matchMedia('(min-width: 800px)');
function handleWidthChange(e) {
if (e.matches) {
// The viewport is at least 800px wide
console.log('Viewport is 800px or wider');
} else {
// The viewport is less than 800px wide
console.log('Viewport is less than 800px');
}
}
// Listen for changes
mq.addEventListener('change', handleWidthChange);
// Initial check
handleWidthChange(mq);
for more info https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Window/matchMedia
How do BEM and mobile-first work together
- BEM and mobile-first complement each other by providing a structured approach to naming CSS classes while ensuring styles are optimized for mobile devices first, then enhanced for larger screens using media queries.
Sample code
.card {
padding: 12px;
font-size: 16px;
}
.card--featured {
background: gold;
}
Last updated on